Today we will learn some SQL. Have you ever used OUTPUT clause in MS SQL? What exactly us the use of OUTPUT clause in MS SQL? What is the advantage of using OUTPUT clause in SQL? All these questions are answered in this article.
What is OUTPUT clause in SQL?
OUTPUT clause gives you the information about each row impacted by running INSERT or UPDATE or DELETE or MERGE SQL statement. Normally in applications we use this information to return to the user in a meaningful manner to show the result of submitting the data.
What you can do is, you may save this information in a temporary table or in a permanent table itself for future use. You can use this information for auditing purpose also because it has got complete information about the sol statement which you executed row by row.
The main disadvantage of this OUTPUT clause is it returns the same information even if your SQL execution throws error or it is rolled back. So you need to make sure that such information should not be used for any auditing purpose or to pass the information to client.
Now lets see what kind of information we gets when we use OUTPUT clause.
First we will create a sample table.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[tblBill](
[BillDate] [datetime] NULL,
[Expense] [numeric](18, 0) NULL,
[travel] [numeric](18, 0) NULL
)
GO
Lets query the table and see the values we have inserted in this table.

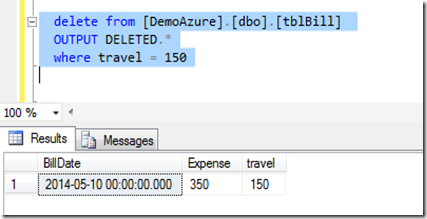
Now we will delete one row with the OUTPUT clause and see the result and also the syntax to use output clause.
delete from [DemoAzure].[dbo].[tblBill]
OUTPUT DELETED.*
where travel = 150
As you can see above OUTPUT clause should be before where clause.
Once you execute this statement it will return the complete row which got deleted like a select statement. This is the reason I mentioned earlier that we can directly insert this values into a table for future use or for auditing purpose.
Lets see the result set now.
Lets see a sample code to insert the value in a table variable.
DECLARE @tblBillVar table(
[BillDate] [datetime] NULL,
[Expense] [numeric](18, 0) NULL,
[travel] [numeric](18, 0) NULL);
INSERT INTO [dbo].[tblBill] ([BillDate],[Expense],[travel])
OUTPUT INSERTED.[BillDate], INSERTED.[Expense], INSERTED.[travel]
INTO @tblBillVar
VALUES ('2015-01-06 00:00:00.000',875,475)
select * from @tblBillVar
Once you execute above query you will find that the inserted values will be displayed in the query analyzer.

Similar to table variable you can have your own table as well.
I hope you are now clear about the OUTPUT clause in MS SQL.